For indoor cannabis cultivation, understanding the correct nutrient balance during the vegetative stage is crucial for healthy, vigorous growth. This blog post will guide you through the essential nutrients—nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (often referred to as potash in the context of fertilizers)—along with environmental factors like pH, EC, VPD, and CO2, and provide a sample feeding schedule.
The Role of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium in Vegetative Growth
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants prioritize developing strong stems, lush leaves, and robust root systems. This growth is heavily supported by three primary macronutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K).
Nitrogen (N): The Engine of Green Growth Nitrogen is the most critical nutrient during the vegetative phase. It's a key component of chlorophyll, the molecule responsible for photosynthesis, and a building block for amino acids, proteins, and enzymes. Adequate nitrogen leads to vibrant, dark green leaves and vigorous overall growth.
Phosphorus (P): The Energy Transfer Facilitator While less dominant than nitrogen in the vegetative stage, phosphorus plays a vital role in energy transfer within the plant. It's essential for photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and the development of strong root systems. Healthy roots are the foundation for a healthy plant.
Potassium (K): The All-Around Regulator Potassium, often referred to as potash in the context of fertilizer, is a powerhouse nutrient that regulates numerous plant functions. It strengthens cell walls, improves water uptake and nutrient transport, enhances disease resistance, and plays a role in enzyme activation. A well-nourished plant with sufficient potassium will be more resilient and better prepared for the flowering stage.
Understanding EC and pH
Electrical Conductivity (EC): Measuring Nutrient Strength EC measures the electrical conductivity of your nutrient solution, indicating the total concentration of dissolved salts (nutrients). For cannabis in the vegetative stage, a target EC range typically falls between 1.2 and 1.8 mS/cm, depending on the plant's age and vigor. Monitoring EC helps prevent over or under-feeding.
pH Level:
The Key to Nutrient Availability pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of your nutrient solution. For most hydroponic or soilless cannabis grows, an ideal pH range for the vegetative stage is between 5.8 and 6.2. If the pH is too high or too low, even if nutrients are present, the plant won't be able to absorb them efficiently, leading to deficiencies.
Environmental Controls: CO2 and VPD

CO2 Levels: Boosting Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a vital ingredient for photosynthesis. In an indoor grow, supplementing CO2 can significantly increase growth rates and yields, especially when light levels and temperatures are optimized. During the vegetative stage, aiming for CO2 levels between 800 and 1200 PPM (parts per million) can be highly beneficial. This typically requires a CO2 generator or tank and a controller.
Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD): Optimizing Transpiration VPD measures the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and how much moisture the air can hold when it's saturated. It's a crucial metric for understanding plant transpiration and overall health. For the vegetative stage of cannabis, an optimal VPD range generally falls between 0.8 and 1.2 kPa. Maintaining the correct VPD encourages efficient water and nutrient uptake.
Sample Vegetative Feeding Schedule
This is a general guideline and should be adjusted based on your specific strain, growing medium, and plant observations. Always observe your plants for signs of nutrient excess or deficiency.
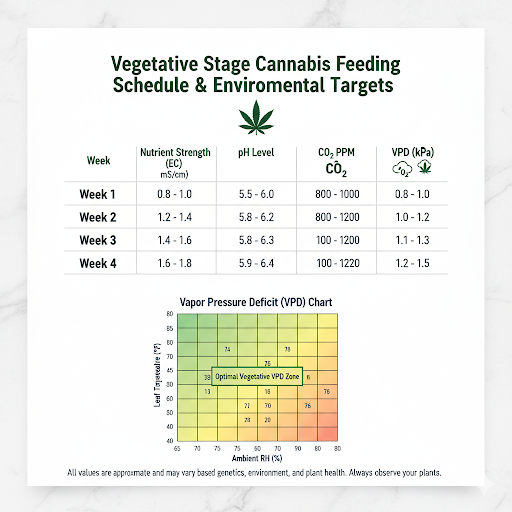
| Week | Nutrient Strength (EC mS/cm) | pH Level | CO2 PPM | VPD (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8 - 1.0 | 5.5 - 6.0 | 800 - 1000 | 0.8 - 1.0 |
| 2 | 1.2 - 1.4 | 5.8 - 6.2 | 800 - 1200 | 1.0 - 1.2 |
| 3 | 1.4 - 1.6 | 5.8 - 6.3 | 1000 - 1200 | 1.1 - 1.3 |
| 4 | 1.6 - 1.8 | 5.9 - 6.4 | 1000 - 1200 | 1.2 - 1.5 |
Note: Always use high-quality nutrients specifically formulated for cannabis. Calibrate your EC and pH meters regularly.
Nutrient Delivery Systems
For indoor cultivation, efficient nutrient delivery is key. Many growers utilize reservoirs and irrigation systems to provide consistent feeding.
By diligently managing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels, along with critical environmental factors like pH, EC, CO2, and VPD, you can ensure your cannabis plants thrive during their vegetative stage, setting the foundation for a successful and abundant harvest.





